The TFT Color Monitor is a common display technology used in various devices. Its vibrant colors and sharp images make it popular in computers and televisions. This monitor uses thin-film transistor (TFT) technology to enhance image quality and responsiveness.
A TFT Color Monitor works by controlling individual pixel colors through tiny transistors. Each pixel on the screen is made up of red, green, and blue sub-pixels. Together, these blend to create a wide range of colors. Users often appreciate the clarity and brightness provided by this technology. However, some may notice limitations in viewing angles and color accuracy.
While TFT monitors have many benefits, they are not without flaws. Color distortion can occur when viewed from different angles. This can be frustrating for users who depend on precise color representations. Understanding how a TFT Color Monitor operates can help users make better choices in display technologies.
A TFT color monitor utilizes thin-film transistor technology to enhance display performance. This type of monitor features a grid of transistors that control individual pixels. Each pixel's color is determined by varying the intensity of red, green, and blue subpixels. This setup results in sharp images and vibrant colors, crucial for applications like graphic design and gaming.
According to industry reports, the TFT monitor market has shown significant growth, with a projected increase of 6% annually until 2025. Despite its advantages, TFT technology faces challenges. Viewing angles can be limited, leading to color distortion from different perspectives. Moreover, the production process can be costly and environmentally taxing.
Users often note performance discrepancies in bright lighting conditions. This limits where and how TFT monitors can be effectively used. Manufacturers continue to refine the technology, tackling issues like power consumption and response time. The evolution of TFT displays must balance quality, cost, and sustainability to maintain relevance in a competitive market.
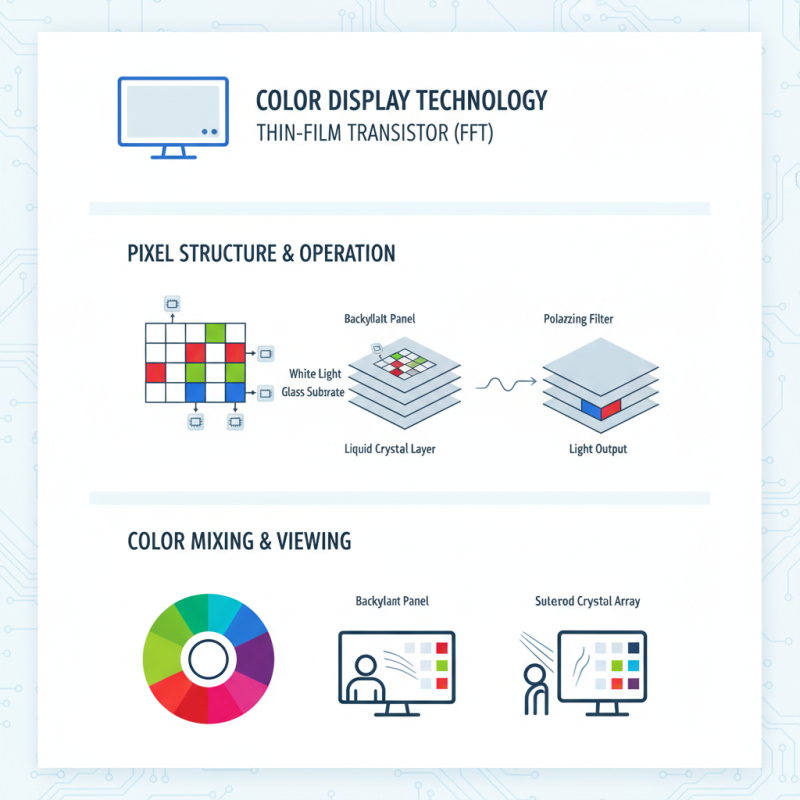
TFT color monitors rely on thin-film transistor technology. This approach helps in controlling pixels effectively. A key component is the liquid crystal display (LCD) layer. It transforms electrical signals into visual images. By manipulating light passing through liquid crystals, vibrant colors emerge on the screen.
Another important part is the backlight. It illuminates the monitor, enabling clear visibility. Typically, LED lights are used for this purpose. They produce bright, even lighting, enhancing color accuracy. However, some may find that backlighting can cause glare. Adjustments may be needed based on the environment.
When using a TFT monitor, keep in mind that screen resolution matters. Higher resolutions produce sharper images. This is important for graphic design and video editing. Consider adjusting brightness and contrast settings to improve visibility. If colors seem off, recalibrating might be necessary. Regular maintenance helps to ensure optimal performance.
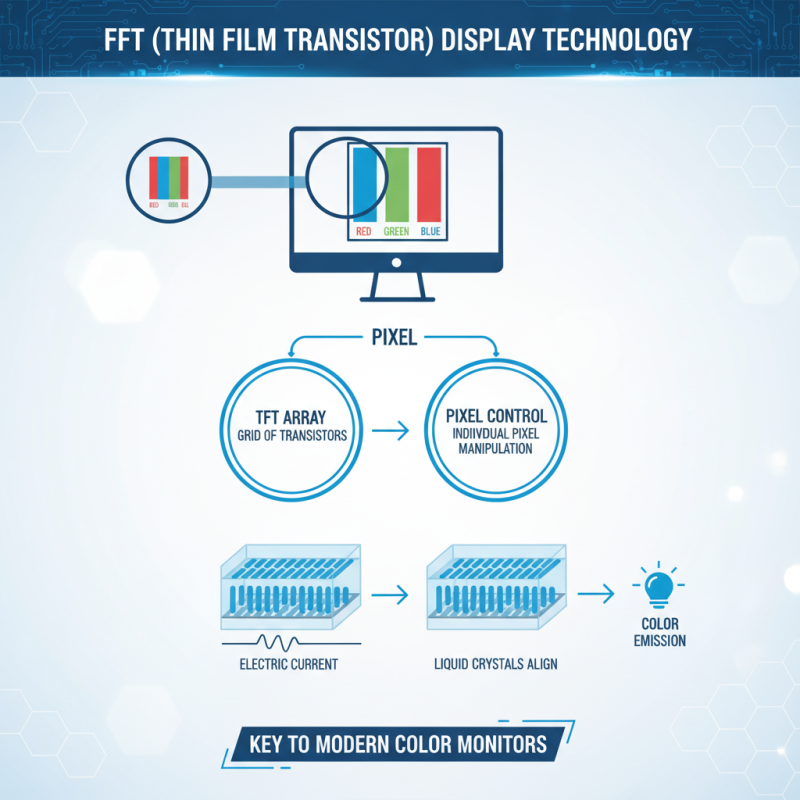
TFT, or Thin Film Transistor technology, is central to many modern color monitors. It uses a grid of tiny transistors to control individual pixels. Each pixel can emit different colors, creating the vibrant images we see. This technology relies on liquid crystals, which align when an electric current passes through them.
The process starts with a backlight that illuminates the screen. As light passes through the layers of the monitor, it reaches the liquid crystals. These crystals twist in response to electrical signals. By varying the voltage, the amount of light passing through each pixel changes. This creates the diverse colors displayed on the screen.
Despite its advancements, TFT technology isn't perfect. Color reproduction can suffer from viewing angles. The monitor may look different when viewed from the side. Also, the response time can lag, leading to motion blur in fast-paced scenes. These issues remind us that while TFT monitors are a leap forward, they still have room for improvement.
TFT color monitors have transformed the way we experience visuals. These screens use thin film transistor technology to produce vibrant images. One significant advantage is their superior image quality. The colors are bright and the contrast is sharp, making everything from movies to games look stunning.
Another benefit is the reduced response time. This is essential for gaming and video playback. With faster refresh rates, motion appears smoother. However, there are times when colors may not look accurate in bright light. It’s a common challenge that users face.
TFT monitors also occupy less space, making them ideal for small workstations. They can be lighter than traditional displays, too. Yet, we should consider the viewing angles. Sometimes, the colors change when viewed from different perspectives. All these factors contribute to how we appreciate technology in our daily lives.
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Technology | Thin Film Transistor (TFT) |
| Resolution | 1920 x 1080 (Full HD) |
| Color Depth | 24-bit (16.7 million colors) |
| Response Time | 5 ms |
| Viewing Angle | Horizontal: 170°, Vertical: 160° |
| Power Consumption | 50 Watts |
| Weight | 3.2 kg |
| Advantages | High color accuracy, fast response time, low power consumption, and slim design. |
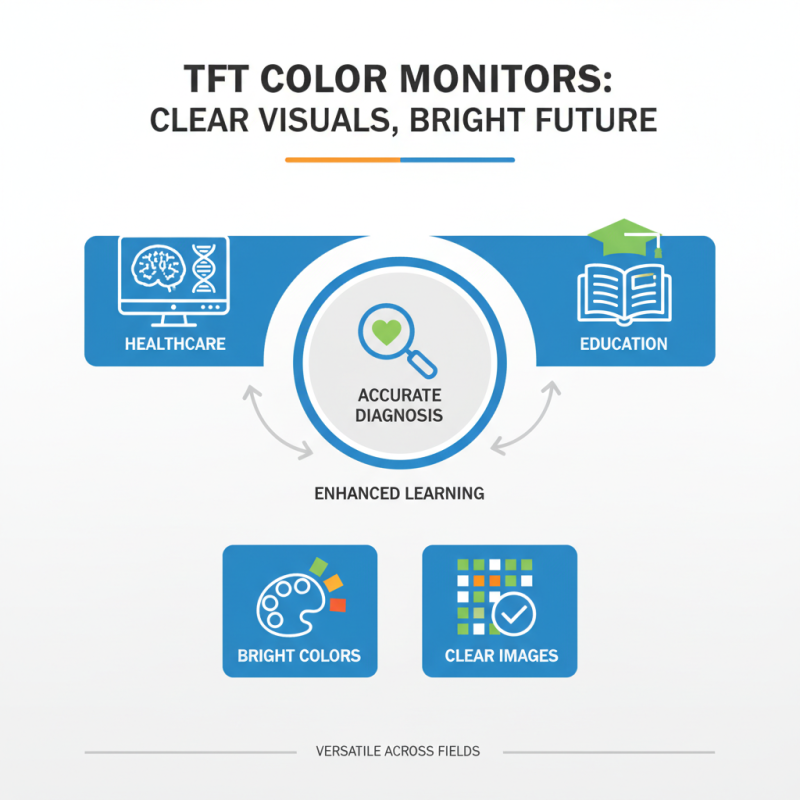
TFT color monitors are widely used across various fields. They offer bright colors and clear images. In healthcare, TFT monitors display detailed medical images. Doctors rely on these visuals for accurate diagnoses. In the education sector, they enhance learning experiences. Students engage better with vibrant, interactive content.
In retail, TFT displays showcase products attractively. They captivate customers' attention. However, not every store uses them effectively. Poor placement or dull content can leave customers uninterested. It’s crucial for retailers to continuously update their displays to maintain engagement.
Tip: Regularly refresh your content. Stale visuals can lead to decreased interest. In transportation, TFT monitors are used for navigation and information displays. They provide real-time updates, which is essential for passengers. Yet, sometimes these systems can be slow to respond, causing frustration. Reflecting on user experience is vital for improvement.